
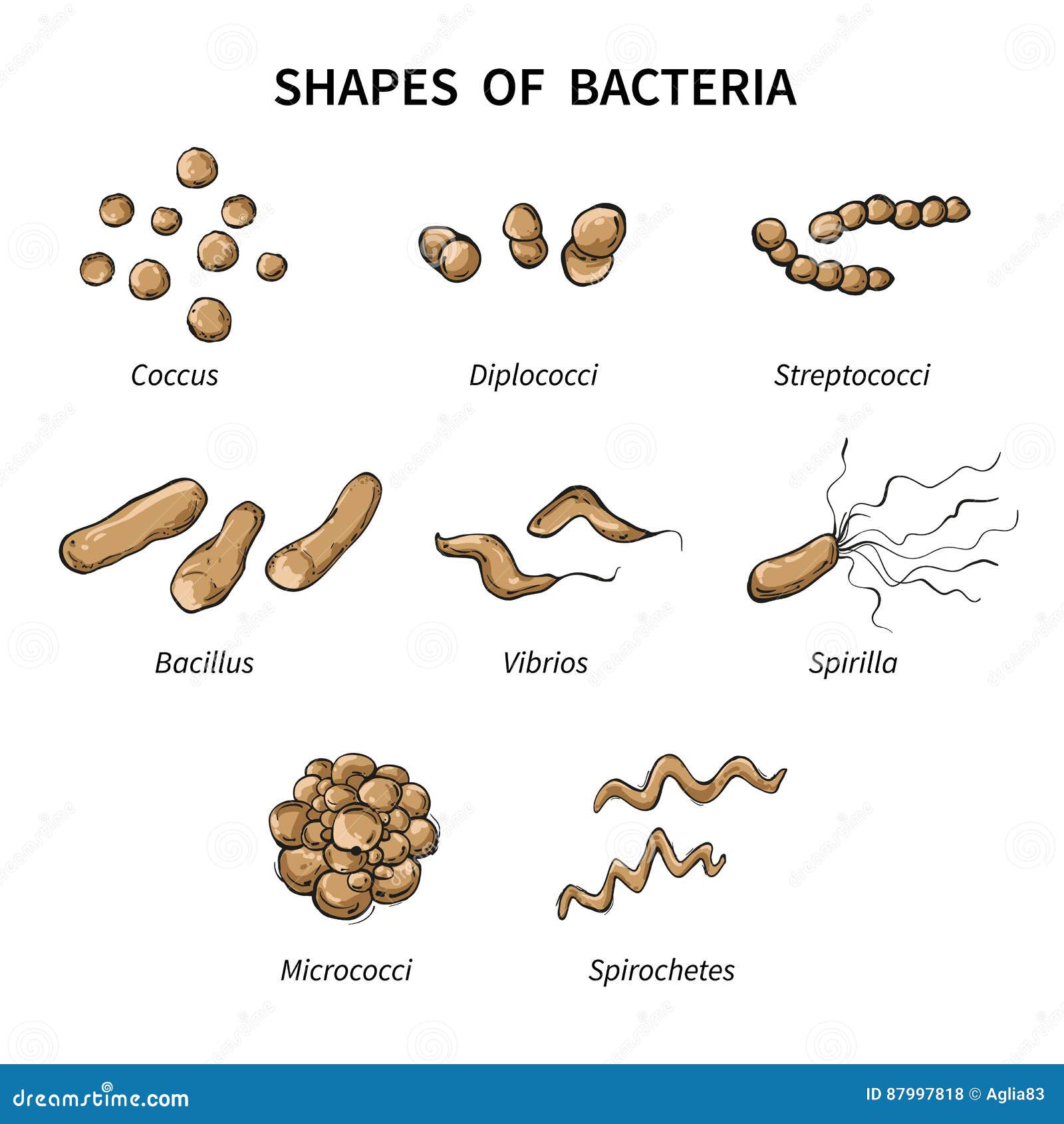
Colonies are described based on size, shape, texture, elevation, pigmentation, and effect on growth medium.

They come in four basic shapes: spherical (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli), arc-shaped (vibrio), and spiral (. Leptospira species, which cause leptospirosis. Colony morphology can sometimes be useful in bacterial identification. Bacteria are complex and highly variable microbes.Owing to their morphological properties, spirochetes are difficult to Gram-stain but may be visualized using dark field microscopy or Warthin–Starry stain. Spirochetes Thin spirochete Treponema pallidum bacteria, the causative agent of syphilis magnified 400 times.Ī spirochete (plural spirochetes) is a very thin, elongate, flexible, spiral bacteria that is motile via internal periplasmic flagella inside the outer membrane. The cocci are round, the bacilli are rods, and the. The shape, size, and pigmentation of the colonies are the characteristics that determine. Bacteria are classified by shape into three basic groups: cocci, bacilli, and spirochetes (Figure 21). However, there are some that hold this to range between 1 and 10 micrometers. Some of the bacterial colonies are colored, some are circular in shape, and a few others are irregular. Helicobacter species, such as Helicobacter pylori, a cause of peptic ulcers According to many microbiology books, the average size of most bacteria is between 0.2 and 2.0 micrometer (diameter).Coccobacillus: Oval and similar to coccus (circular shaped bacterium). Streptobacilli: Bacilli arranged in chains. 2 Diplobacilli: Two bacilli arranged side by side with each other. Campylobacter species, such as Campylobacter jejuni, a foodborne pathogen that causes campylobacteriosis 1 Bacilli usually divide in the same plane and are solitary, but can combine to form diplobacilli, streptobacilli, and palisades.Spirillum Campylobacter jejuni is a common pathogen of bacterial food-related gastrointestinal illness.Ī spirillum (plural spirilla) is a rigid spiral bacterium that is Gram-negative and frequently has external amphitrichous or lophotrichous flagella. The two types of spiral cells are spirillum and spirochete, with spirillum being rigid with external flagella, and spirochetes being with internal flagella. Spiral bacteria can be subclassified by the number of twists per cell, cell thickness, cell flexibility, and motility. Bacteria are classified by shape into three primary groups: cocci, bacilli, and spiral-shaped. Spiral bacteria, bacteria of spiral ( helical) shape, form the third major morphological category of prokaryotes along with the rod-shaped bacilli and round cocci.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
