
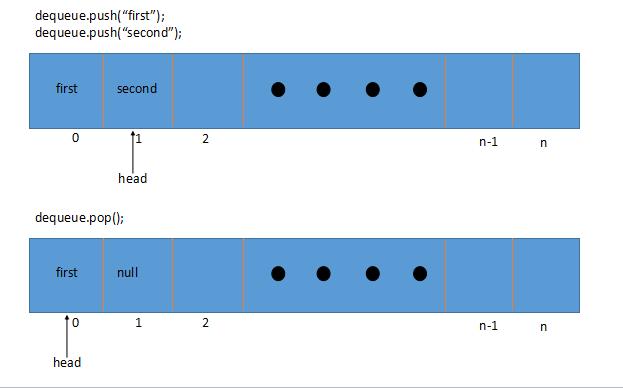
The key characteristic is that producers may wait for consumers to receive elements. TransferQueue is a type of BlockingQueue tailored for the producer-consumer pattern. It provides methods in four different forms – one throws an exception, second returns null or false value, third blocks current thread indefinitely until operation completion, and fourth blocks for only the specified maximum time limit. It provides methods in four different forms – one throws an exception, second returns null or false value, third blocks current thread indefinitely until operation completion, and fourth blocks for only the specified maximum time limit.īlockingQueue supports additional blocking operations that wait for Queue to become non-empty when retrieving an element and wait for space to become available while storing an element. Just like the traditional Queue, the Dequeue provides methods to add, retrieve and peek at elements from both the ends.īlockingDequeue supports additional blocking operations that wait for Dequeue to become non-empty when retrieving an element and wait for space to become available while storing an element. While majority of Dequeue implementations don’t have a fixed limit on the number of elements, however, this interface is flexible to support both capacity-restricted dequeues and those with no fixed size limit. The Queue interface has 4 main sub-interfaces and several Java Queues provide implement it:ĭequeue is a linear collection that supports element insertion and removal from both the ends. If the queue is empty, the element() method throws NoSuchElementException whereas the peek() method returns null value.
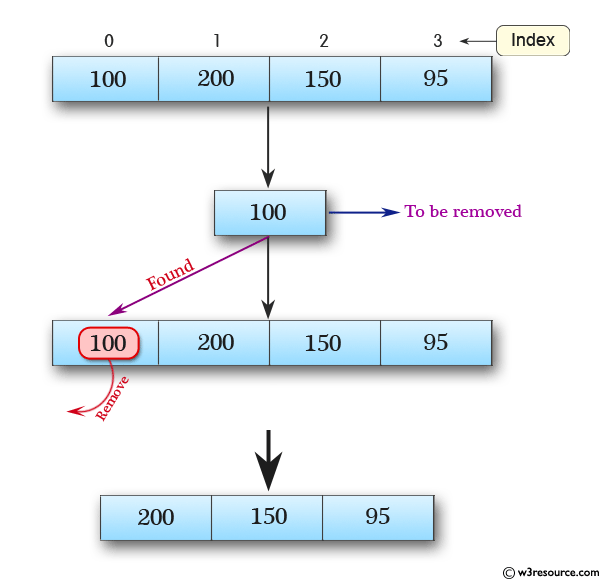

Java Queue interface is a subtype of Collection interface, so all methods of Collection interface are also available in the Queue interface. The figure below illustrates the insertion and removal elements from queue: Shoppers who came first are billed first and those who came later are billed later.
After shoppers pick up items to be purchased, they form an orderly line in front of the billing counter. A real-life analogy could be shoppers in a supermarket like Walmart. Java Queue interface is part of and provides first-in-first-out (FIFO) access of member elements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
